Welcome to Visit Canvey Island Places
The Walkfo guide to things to do & explore in Canvey Island
![]() Visit Canvey Island places using Walkfo for free guided tours of the best Canvey Island places to visit. A unique way to experience Canvey Island’s places, Walkfo allows you to explore Canvey Island as you would a museum or art gallery with audio guides.
Visit Canvey Island places using Walkfo for free guided tours of the best Canvey Island places to visit. A unique way to experience Canvey Island’s places, Walkfo allows you to explore Canvey Island as you would a museum or art gallery with audio guides.
Visiting Canvey Island Walkfo Preview
Canvey Island is a civil parish and reclaimed island in the Thames estuary, near Southend-on-Sea in Essex, England. It has an area of 7.12 square miles (18.44 km) and a population of 38,170. The island was mainly agricultural land until the 20th century, when it became the fastest-growing seaside resort in Britain. When you visit Canvey Island, Walkfo brings Canvey Island places to life as you travel by foot, bike, bus or car with a mobile phone & headphones.
Canvey Island Places Overview: History, Culture & Facts about Canvey Island
Visit Canvey Island – Walkfo’s stats for the places to visit
With 21 audio plaques & Canvey Island places for you to explore in the Canvey Island area, Walkfo is the world’s largest heritage & history digital plaque provider. The AI continually learns & refines facts about the best Canvey Island places to visit from travel & tourism authorities (like Wikipedia), converting history into an interactive audio experience.
Canvey Island history
Roman

Excavations have unearthed a collection of early man-made objects from the Neolithic era, a bracelet dating from the Bronze Age, and Iron Age pottery. However, the remains of Roman structures and objects suggests the first settlement of Canvey occurred between AD 50 and 250. The remains point to a community existing with a farmstead, a garrison, a burial ground, and a large salt-making industry.
Saxon and medieval
The area of Canvey was recorded in the Domesday Book as a sheep-farming pasture under the control of nine parishes across south inland and coastal Essex. The name of the island is derived from the Anglo-Saxon Caningaege, meaning “the Island of Cana’s People”
Tudor divisions

The Sheppey insula is a close eastern division which is perhaps the part which later almost wholly merged into the present island. The Trinovantes, Cantiaci and the Catuvellauni counselled with the Iceni shortly before staging Boudicca’s rebellion against the Romans. Two Tree Island to the north is also recognisable, if halved in length.
14th century – 17th century

During Edward II’s reign (1307–1327) the land was under the possession of John de Apeton and the first attempts were made at managing the effects of the sea with rudimentary defences. In 1622, Sir Henry Appleton and Canvey’s other landowners instigated a project to reclaim the land and wall the island from the Thames. The engineers successfully reclaimed 3,600 acres (15 km) by walling the island with local chalk, limestone and the heavy clay of the marshes, with the main length along the Thames faced with Kentish ragstone.
Modern era
The Chapman Lighthouse, briefly described in Joseph Conrad’s novel Heart of Darkness, was on the coast of Canvey Island. It is believed that the peril of the mudflats below such shallow waters off the Canvey Island coast prompted the Romans to devise some form of beacon as a warning in the area. In 1851 a hexagonal lighthouse was constructed by the engineer James Walker, a consultant lighthouse engineer at Trinity House at the time. This all-iron lighthouse replaced a lightship which had been moored in the area for the preceding four years. The lighthouse was demolished in 1957–1958 because of its poor condition. The Lobster Smack Inn saw many bare-knuckle fights in the 1850s, but few as dramatic as that between Tom ‘the Brighton Boy’ Sayers (1826–65) and Aaron Jones on 6 January 1857. The fight lasted for three hours and 65 rounds, and was finally declared a draw when it became too dark to see. Sayers won at the rematch a month later in London. Sometimes the bouts were between local families, the best known being that between champion Ben Caunt and Nat Langham. The fight arose from a family feud and Caunt took Langham to 60 rounds in September 1853. Langham was knocked down 59 times during the bout and because, it is said, of his sportsmanship Caunt agreed to settle their differences with a handshake. Philip Benton reported about Canvey Chapel in 1867: “The seats are open and unappropriated, except one, which is set apart for the officer and the men under him of the Preventive Service; there being a station on the island for nine men, an officer and a chief boatman.” The Preventive Men had their own special row of cottages close to the seafront near the old Lobster Smack Inn. That ancient pub was itself described by Charles Dickens in Great Expectations. So out of the way (and therefore the smugglers) was the inn behind the sea wall, in the 18th century it was known as ‘The World’s End’. In the 19th century, the isolation made it an ideal point for the meetings of pugilists. The row of Preventive Men’s Cottages has survived against the odds. Today they are surrounded by a small housing estate. During the Victorian era Canvey became a very fashionable place to visit, and its air was promoted as having healing properties. This started in 1899, after the Black Monday floods, when an entrepreneur called Frederick Hester bought Leigh Beck Farm, and started what was to be called Southview Park estate. The properties sold very quickly so Frederick bought more plots of land, selling them as dream homes for London’s Eastenders. Hester wanted to create Canvey as a great seaside resort for Londoners, and so built the first promenade, a pier and a magnificent winter garden and palace, which he planned to cover six miles (but only covered a mile), as well as a monorail system (initially horse-drawn then later electric). Hester marketed Canvey as “Ye Old Dutch Island”, giving many of the new roads Dutch-sounding names and enticing potential buyers with free rail tickets. The project started well with thousands of plots sold, but by 1905 had fallen apart due to materials not being delivered and issues with land ownership with the laying of the monorail. Hester was declared bankrupt and everything was sold off at an auction held at Chimney’s Farm. A new seafront was developed in the 1930s, with Canvey Casino – an amusement arcade and park – opening as the first building on what would become Eastern Esplanade. Since then further amusements, a cinema, the pioneering Labworth Cafe, the Monico pub and nightclubs such as the Goldmine were built. Canvey Island remained a popular holiday and weekend destination until the cheap foreign package holiday became popular in the 1970s. During the Second World War the island was a part of the GHQ Line, a line of concrete pillboxes constructed as a part of the defence against the expected German invasion. Some of the old pillboxes are still in place. Also, concrete barges were used extensively just off the south coast of the island, partly as a sea-barrier and also as a mounting point for anti-aircraft guns; one of which was beached on the east end of the island and remained for many years as a point of interest for visitors and a play area for many generations of the island’s children. It has since been demolished by the Island Yacht Club as it was considered dangerous. Along with the Coalhouse Fort at nearby East Tilbury, Thorney Bay on the southern coast of the island was the site of a degaussing station built to monitor the effectiveness of the equipment on board the allied ships passing along the Thames. The structure is the last intact degaussing station on the north side of the river, and was still operating in 1974. Known as the Canvey loop, the building was occupied by the Women’s Royal Naval Service and used for monitoring merchant ships. The building has since been re-opened as a museum dubbed the “Bay Museum” and has First World War exhibits on the ground floor and Second World War exhibits on the first floor. The Commonwealth War Graves Commission records four civilian residents of Canvey Island Urban District died as a result of enemy action during the war. On 1 February 1953, the infamous North Sea Flood hit the island during the night and caused the deaths of 58 people. Many of the victims were in the holiday bungalows of the eastern Newlands estate and perished as the water reached ceiling level. The small village area of the island is approximately two feet (60 cm) above sea level and consequently escaped the effects of the flood. This included the Red Cow pub, which was later renamed the King Canute in reference to the legend of the 11th-century Danish king of England commanding the tide to halt with the sea lapping at his feet. The King Canute pub was closed in May 2014. In 2016 a scheme to convert the building into retail space and apartments was proposed. After the flooding of 1953, a new seawall was built, which was then replaced with a significantly larger construction in the 1980s. The southern area of the Canvey Island West ward at Hole Haven has predominantly existed as petrochemical site since the first construction of an oil terminal there in 1936. In 1959, as part of a pioneering Anglo-American project designed to assess the viability of transporting liquefied natural gas overseas, a gas terminal with two 1000-tonne storage tanks was constructed at the site alongside the oil terminal. The gas terminal built by the British Gas Council was designed to store and distribute imported gas to the whole of Britain via the facilities at Thames Haven and the local refinery at Shellhaven in Coryton. The first delivery of 2,020 tonnes arrived on 20 February 1959 from Lake Charles, Louisiana, by a specially modified liberty ship Normarti renamed The Methane Pioneer. The success of seven further deliveries over the following 14 months established the international industry for transporting liquefied natural gas (LNG) by sea, but the discovery of oil and gas in North Sea limited further British development. Canvey continued to receive 50 shipments of LNG per year from Arzew Algeria, until about 1984, British Gas closed the site in 1994. In 1964 the Italian company Agip Ltd were given an industrial development certificate to build a £15 million oil refinery in the north west of the island. The refinery was never built. In 1972 Occidental Petroleum began construction of an oil refinery. Access roads, about 20 oil-storage tanks, a river jetty and a concrete chimney were constructed, but work was halted in 1975 pending a major design study review following the oil crisis of 1973–4 and OPEC’s increase of oil prices. On 28 March 1973 planning permission was granted to United Refineries Ltd to develop a site to the north of the Occidental refinery site for the construction of another oil refinery. An exploratory public inquiry was held in February/March 1975 into the possible revocation of the planning permission for the United Refineries development. The report of 30 April 1975 recommended revocation and further expert evaluation of the totality of risks facing people who lived in and around Canvey. In March 1976 the Secretaries of State for the Environment and Employment asked the Health and Safety Commission to investigate the risks to health and safety of various installations on Canvey and the neighbouring part of Thurrock. The Commission invited the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) to carry out an investigation. From the Canvey Report (1978) the following hazardous installations were identified: In 1978 the HSE concluded that the residents of the island faced a risk more than five times higher than those in neighbouring South Benfleet. On 27 July 1978 Castle Point District Council asked the Secretary of State “to revoke the planning permission granted to United Refineries Ltd in accordance with his Inspector’s recommendation at the exploratory inquiry in 1975”. The issue of risk was again highlighted in an attack by the IRA in January 1979 on a storage tank at the island’s Texaco oil terminal. A bomb was detonated at a tank containing aviation fuel, but failed to ignite with the fuel escaping into a safety moat. The Occidental site was abandoned in 1975 leaving a half-built oil refinery, storage tanks, and an unused mile-long jetty that cost around £10 million of the approximate total of £60 million spent on the project. However, in the following years the disused and undisturbed site flourished as a haven for wildlife, and in 2003, the final storage tanks were removed in a clean-up operation, and the site was renamed as Canvey Wick and opened as a nature reserve. In September 1997, the celebrity steeplejack Fred Dibnah was hired by Safeway supermarkets to demolish the unused 450-foot (140 m) concrete chimney that was part of the abandoned oil refinery. Safeway had planned for the 2,500-ton chimney to be demolished on 18 September in front of a large crowd of invited guests. This would have been the first time Dibnah’s demolition technique of pit props and fire (without explosives) had been attempted on a concrete chimney and it was also the tallest chimney he had ever attempted to fell. However the chimney unexpectedly collapsed the previous day whilst Dibnah and his team were making the final preparations for the controlled demolition, fortunately without injury. The incident is described in detail in various biographies and by Dibnah himself in his public speaking events afterwards. Dibnah later presented Safeway head office staff with brass paperweights (made from material salvaged from the chimney) stamped “The Great Canvey Island Chimney Disaster 1997”. Calor Gas Ltd now operate the former British Gas site. The site imports, stores, bottles and exports liquified petroleum gases (LPG) propane and butane. There were plans in 2005–7 to convert the plant back to the import of liquified natural gas (LNG) but the planning application was rejected. Oikos Storage Limited now operate the former London & Coastal Wharves Ltd. The site offers a bulk liquid storage facility for refined petroleum products. Neither of the refineries proposed in the 1970s were completed or commissioned. The Occadential site was demolished and the tanks removed, though the former river jetty is still extant.
Canvey Island culture & places
Folklore
The island has only been populated since the 17th century when the Dutch made the marshlands habitable. There are local legends of a Dutchman carrying a sack wandering the northern parts of the island. The story of ‘The Black Man’ and ‘The White Lady’ is believed to be a mythical tale conjured up by smugglers.
Music
Canvey Island was an influential destination in the 1970s for artists of pub rock genre of music such as Graham Parker, Elvis Costello, Eddie and the Hot Rods, Nick Lowe, and The Kursaal Flyers. Peter Green, founding member of Fleetwood Mac, lived on Canvey after leaving the band.
Cultural references
Canvey Island is the setting for the British author Nicola Barker’s 2002 novel Behindlings. The island was also the subject of 2006 Turner Prize nominee Rebecca Warren’s 2003 painted clay sculpture. Canvey was home to a Prada fashion shoot in 2014 starring James McAvoy.
Canvey Island landmarks

The Lobster Smack public house was known to Charles Dickens who mentioned it in Great Expectations. The island is also home to two Dutch Cottages, one in Haven Road and the other on Canvey Road, which were built during the 17th century.
Canvey Island geography / climate
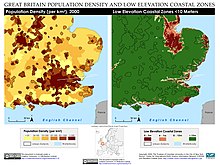
Canvey Island lies off the south coast of Essex 30 miles (48 km) east of London, and 15 miles (24 km) west of Southend-on-Sea. The alluvium was formed in the Holocene period from silt in the River Thames and material entering the estuary on the tides of the North Sea from Norfolk. The island is extremely flat, lying 10 feet (3 m) below mean high water level and consequently is at risk of flooding. Flood defences have been constructed since the Middle Ages, and the first sea wall to completely surround the island was built in 1622.
Why visit Canvey Island with Walkfo Travel Guide App?
![]() You can visit Canvey Island places with Walkfo Canvey Island to hear history at Canvey Island’s places whilst walking around using the free digital tour app. Walkfo Canvey Island has 21 places to visit in our interactive Canvey Island map, with amazing history, culture & travel facts you can explore the same way you would at a museum or art gallery with information audio headset. With Walkfo, you can travel by foot, bike or bus throughout Canvey Island, being in the moment, without digital distraction or limits to a specific walking route. Our historic audio walks, National Trust interactive audio experiences, digital tour guides for English Heritage locations are available at Canvey Island places, with a AI tour guide to help you get the best from a visit to Canvey Island & the surrounding areas.
You can visit Canvey Island places with Walkfo Canvey Island to hear history at Canvey Island’s places whilst walking around using the free digital tour app. Walkfo Canvey Island has 21 places to visit in our interactive Canvey Island map, with amazing history, culture & travel facts you can explore the same way you would at a museum or art gallery with information audio headset. With Walkfo, you can travel by foot, bike or bus throughout Canvey Island, being in the moment, without digital distraction or limits to a specific walking route. Our historic audio walks, National Trust interactive audio experiences, digital tour guides for English Heritage locations are available at Canvey Island places, with a AI tour guide to help you get the best from a visit to Canvey Island & the surrounding areas.
“Curated content for millions of locations across the UK, with 21 audio facts unique to Canvey Island places in an interactive Canvey Island map you can explore.”
Walkfo: Visit Canvey Island Places Map
21 tourist, history, culture & geography spots
Canvey Island historic spots | Canvey Island tourist destinations | Canvey Island plaques | Canvey Island geographic features |
| Walkfo Canvey Island tourism map key: places to see & visit like National Trust sites, Blue Plaques, English Heritage locations & top tourist destinations in Canvey Island | |||
Best Canvey Island places to visit
Canvey Island has places to explore by foot, bike or bus. Below are a selection of the varied Canvey Island’s destinations you can visit with additional content available at the Walkfo Canvey Island’s information audio spots:
 | Castle Point Castle Point is a local government district with borough status in south Essex, 30 miles (48 km) east of central London. The borough comprises the towns and villages of Canvey Island, Hadleigh, South Benfleet, and Thundersley. The median age of residents was in 2011 greater than the national average. |
 | Hadleigh Farm Hadleigh Farm is an educational working farm and cross-country cycling venue located in Hadleigh, within the borough of Castle Point, in the county of Essex. The men’s and women’s mountain biking events of the 2012 Summer Olympics took place on 11 and 12 August. |
 | Church of St Mary the Virgin, South Benfleet The Church of St Mary the Virgin is the parish church of South Benfleet, Essex. The church dates to around the 12th century and predates the neighbouring Hadleigh Castle. It was designated as a Grade I listed building in 1952. |
 | Hadleigh Castle Built after 1215 during the reign of Henry III by Hubert de Burgh, the castle was surrounded by parkland and had an important economic and defensive role. The castle was significantly expanded and remodelled by Edward III, who turned it into a grander property. Built on a soft hill of London clay, it has often been subject to subsidence. |
 | Benfleet F.C. Benfleet Football Club is a football club based in Benfleet, Essex, England. They are currently members of the Eastern Counties League Division One South and play at Park Lane in Canvey Island. |
 | Canvey Wick Canvey Wick is a 93.2 hectare Site of Special Scientific Interest at the south-west corner of Canvey Island in Essex. 18.5 hectares (46 acres) is managed by the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds and Buglife as a nature reserve. |
Visit Canvey Island plaques
![]() 0
0
plaques
here Canvey Island has 0 physical plaques in tourist plaque schemes for you to explore via Walkfo Canvey Island plaques audio map when visiting. Plaques like National Heritage’s “Blue Plaques” provide visual geo-markers to highlight points-of-interest at the places where they happened – and Walkfo’s AI has researched additional, deeper content when you visit Canvey Island using the app. Experience the history of a location when Walkfo local tourist guide app triggers audio close to each Canvey Island plaque. Currently No Physical Plaques.
