Travel to Croydon Map
Croydon tourist guide map of landmarks & destinations by Walkfo
158
travel
spots
![]() When travelling to Croydon, Walkfo’s has created a travel guide & Croydon overview of Croydon’s hotels & accommodation, Croydon’s weather through the seasons & travel destinations / landmarks in Croydon. Experience a unique Croydon when you travel with Walkfo as your tour guide to Croydon map.
When travelling to Croydon, Walkfo’s has created a travel guide & Croydon overview of Croydon’s hotels & accommodation, Croydon’s weather through the seasons & travel destinations / landmarks in Croydon. Experience a unique Croydon when you travel with Walkfo as your tour guide to Croydon map.
Croydon history
Toponymy
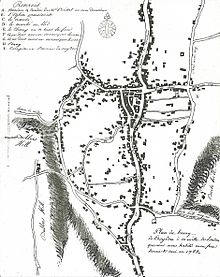
Most place names in the area are of Anglo-Saxon origin . The name Croydon means “crocus” and denu, “valley”, indicating it was a centre for the cultivation of saffron . It has been argued that this cultivation is likely to have taken place in the Roman period .
Early history
The town lies on the line of the Roman road from London to Portslade, and there is some archaeological evidence for small-scale Roman settlement in the area: there may have been a mansio (staging-post) here. Later, in the 5th to 7th centuries, a large pagan Saxon cemetery was situated on what is now Park Lane, although the extent of any associated settlement is unknown. By the late Saxon period Croydon was the hub of an estate belonging to the Archbishops of Canterbury. The church and the archbishops’ manor house occupied the area still known as “Old Town”. The archbishops used the manor house as an occasional place of residence: as lords of the manor they dominated the life of the town well into the early modern period, and as local patrons they continue to have an influence. Croydon appears in Domesday Book (1086) as Croindene, held by Archbishop Lanfranc. Its Domesday assets included 16 hides and 1 virgate of land; a church; a mill worth 5s; 38 plough-teams; 8 acres (3.2 ha) of meadow; and woodland for 200 hogs. It had a recorded population of 73 households (representing roughly 365 individuals); and its value in terms of taxes rendered was £37 10s 0d. The church had been established in the middle Saxon period, and was probably a minster church, a base for a group of clergy living a communal life. A charter issued by King Coenwulf of Mercia refers to a council that had taken place close to the monasterium (meaning minster) of Croydon. An Anglo-Saxon will made in about 960 is witnessed by Elfsies, priest of Croydon; and the church is also mentioned in Domesday Book. The will of John de Croydon, fishmonger, dated 6 December 1347, includes a bequest to “the church of S John de Croydon”, the earliest clear record of its dedication. The church still bears the arms of Archbishop Courtenay and Archbishop Chichele, believed to have been its benefactors. In 1276 Archbishop Robert Kilwardby acquired a charter for a weekly market, and this probably marks the foundation of Croydon as an urban centre. Croydon developed into one of the main market towns of north east Surrey. The market place was laid out on the higher ground to the east of the manor house in the triangle now bounded by High Street, Surrey Street and Crown Hill. By the 16th century the manor house had become a substantial palace, used as the main summer home of the archbishops and visited by monarchs and other dignitaries. However, the palace gradually became dilapidated and surrounded by slums and stagnant ponds, and in 1781 the archbishops sold it, and in its place purchased a new residence at nearby Addington. Nevertheless, many of the buildings of the original Croydon Palace survive, and are in use today as Old Palace School. The Parish Church (now Croydon Minster) is a Perpendicular-style church, which was remodelled in 1849 but destroyed in a great fire in 1867, after which only the tower, south porch, and outer walls remained. A new church was designed by Sir George Gilbert Scott, one of the greatest architects of the Victorian age, and opened in 1870. His design loosely followed the previous layout, with knapped flint facing and many of the original features, including several important tombs. Croydon Parish Church is the burial place of six Archbishops of Canterbury: John Whitgift, Edmund Grindal, Gilbert Sheldon, William Wake, John Potter and Thomas Herring. Historically part of the Diocese of Canterbury, Croydon is now in the Diocese of Southwark. In addition to the suffragan Bishop of Croydon, the Vicar of Croydon is an important preferment. Addington Palace is a Palladian-style mansion between Addington Village and Shirley, in the London Borough of Croydon. Six archbishops lived there between 1807 and 1898, when it was sold. Between 1953 and 1996 it was the home of the Royal School of Church Music. It is now a conference and banqueting venue. Croydon was a leisure destination in the mid 19th century. In 1831, one of England’s most prominent architects, Decimus Burton, designed a spa and pleasure gardens below Beulah Hill and off what is now Spa Hill in a bowl of land on the south-facing side of the hill around a spring of chalybeate water. Burton was responsible for the Beulah Spa Hotel (demolished around 1935) and the layout of the grounds. Its official title was The Royal Beulah Spa and Gardens. It became a popular society venue attracting crowds to its fêtes. One widely publicised event was a “Grand Scottish Fete” on 16 September 1834 “with a tightrope performance by Pablo Fanque, the black circus performer who would later dominate the Victorian circus and achieve immortality in The Beatles song, Being for the Benefit of Mr. Kite!” The spa closed in 1856 soon after the opening nearby of the Crystal Palace which had been rebuilt on Sydenham Hill in 1854, following its success at the Great Exhibition in Hyde Park. It was destroyed in a spectacular fire in 1936. Horse racing in the area took place occasionally, notably during visits of Queen Elizabeth I to the archbishop. Regular meetings became established first on a course at Park Hill in 1860 and from 1866 at Woodside, where particularly good prizes were offered for the races run under National Hunt rules. In that sphere its prestige was second only to Aintree, home of the Grand National. Increasing local opposition to the presence of allegedly unruly racegoers coupled with the need to obtain a licence from the local authority led to it being closed down in 1890. The Elizabethan Whitgift Almshouses, the “Hospital of the Holy Trinity”, in the centre of Croydon at the corner of North End and George Street, were erected by Archbishop John Whitgift. He petitioned for and received permission from Queen Elizabeth I to establish a hospital and school in Croydon for the “poor, needy and impotent people” from the parishes of Croydon and Lambeth. The foundation stone was laid in 1596 and the building was completed in 1599. The premises included the Hospital or Almshouses, providing accommodation for between 28 and 40 people, and a nearby schoolhouse and schoolmaster’s house. There was a Warden in charge of the well-being of the almoners. The building takes the form of a courtyard surrounded by the chambers of the almoners and various offices. Threatened by various reconstruction plans and road-widening schemes, the Almshouses were saved in 1923 by intervention of the House of Lords. On 21 June 1983 Queen Elizabeth II visited the Almshouses and unveiled a plaque celebrating the recently completed reconstruction of the building. On 22 March each year the laying of the foundation stone is commemorated as Founder’s Day. The Grade II listed West Croydon Baptist Church was built in 1873 by J. Theodore Barker. It is a red brick building with stone dressings. Its three bays are divided by paired Doric pilasters supporting a triglyph frieze and panelled parapet. The Parish Church of St Michael and All Angels by John Loughborough Pearson in West Croydon was built between 1880 and 1885, and is Grade I listed.
Industrial Revolution and the railway

Croydon became the terminus of two pioneering commercial transport links with London . The arrival of the railways and other communications advances in the 19th century led to a 23-fold increase in the town’s population between 1801 and 1901 . The rapid expansion of the town led to considerable health problems, especially in the damp and overcrowded working class district of Old Town .
A growing town

In 1883 Croydon was incorporated as a borough . In 1889 it became a county borough, with a greater degree of autonomy . During the Second World War, much of central Croydon was devastated by German V-1 flying bombs and V-2 rockets . After the war, Heathrow Airport superseded the town as London’s main airport . By the 1950s the town was becoming congested, and the Council decided on another major redevelopment scheme .
Modern Croydon

The Fairfield Halls arts centre and event venue opened in 1962 . No. 1 Croydon (formerly the NLA Tower) designed by Richard Seifert & Partners was completed in 1970 . The Warehouse Theatre opened in 1977 . The Prospect West office development was built in 1991 to 1992 and its remodelling planned in 2012 has now been completed .
Future

Croydon Vision 2020 plan includes new office blocks, apartment buildings, shopping centres and other developments . More than 2,000 new homes are planned, with Tramlink getting more tracks, platforms and trams . Fairfield Halls is to become the linchpin of a cultural quarter encompassing nearby College Green .
Croydon map & travel guide with history & landmarks to explore
Visit Croydon Walkfo Stats
With 158 travel places to explore on our Croydon travel map, Walkfo is a personalised tour guide to tell you about the places in Croydon as you travel by foot, bike, car or bus. No need for a physical travel guide book or distractions by phone screens, as our geo-cached travel content is automatically triggered on our Croydon map when you get close to a travel location (or for more detailed Croydon history from Walkfo).
| Travel Location: Travel Area: | Croydon [zonearea] | Audio spots: Physical plaques: | 158 30 | Population: | [zonesize] |
|---|
Average seasonal temperatures at zone
Tourist Guide to Croydon Map
Croydon map historic spot | Croydon map tourist destination | Croydon map plaque | Croydon map geographic feature |
| Walkfo Croydon travel map key: visit National Trust sites, Blue Plaques, English Heritage locations & top travel destinations in Croydon | |||